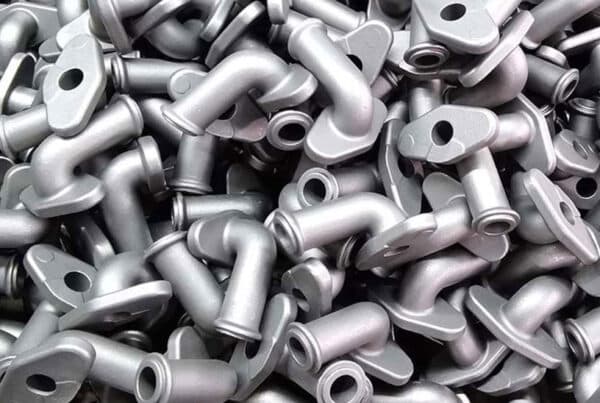
Die casting is one of the most advanced and widely used methods in the metal parts manufacturing industry, which is used in various industries including automotive, aerospace, electronics and machinery due to its high precision, excellent quality and mass production capability. In this article, we will comprehensively review die casting, its steps, advantages, disadvantages, applications and its difference from other casting methods. If you are looking for detailed and practical information about this process, stay with us.
What is die casting?
Die casting or pressure casting (Die Casting) is a process in which molten metal is injected into metal molds at high pressure. This method helps produce parts with high dimensional accuracy, smooth surfaces and complex details. Die casting is usually used for non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium and copper. This process is divided into two main types:
Hot Chamber Die Casting: Suitable for metals with low melting points such as zinc and magnesium.
Cold Chamber Die Casting: For metals with high melting points such as aluminum and copper.
The word “die casting” is a combination of the two English words “Die” and “Casting” and means casting using metal molds.
Die Casting Process Steps
The die casting process consists of several key steps, each of which plays an important role in the final quality of the product:
Die preparation: Die casting molds are usually made of steel and are divided into two fixed and moving parts. Before injection, the mold is coated with lubricants to make it easier to remove the part.
Metal melting: The desired metal (such as aluminum or zinc) is melted in a furnace and reaches the appropriate temperature.
Molten metal injection: Molten metal is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure (between 1,000 and 30,000 psi).
Cooling and solidification: The molten metal cools inside the mold and solidifies.
Part ejection: After solidification, the mold is opened and the final part is ejected.
Final finishing: The part may require additional cutting, polishing, or coating.
These steps are performed at high speed and allow for high-volume production of parts.
Advantages of die casting
Pressure casting is very popular in various industries due to its unique characteristics. Some of its most important advantages are:
High accuracy: Parts produced with die casting have precise tolerances and intricate details.
Smooth and high-quality surface: Die cast parts require less finishing operations.
Mass production: This method is very cost-effective for producing parts in large numbers.
Material diversity: Possibility of using different metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.
High strength: Die cast parts usually have good mechanical strength.
Waste Reduction: Due to the precision of the process, waste of raw materials is minimized.
Disadvantages of Die Casting
Despite its many advantages, die casting also has disadvantages that must be considered:
High initial cost: Making die casting molds is expensive and is not cost-effective for small-scale production.
Limitations in part size: Die casting is not suitable for large parts.
Material limitations: This method is more applicable to non-ferrous metals and is less used for ferrous metals.
Possible defects: If not carefully controlled, problems such as gas cavities or cracks may occur in the parts.
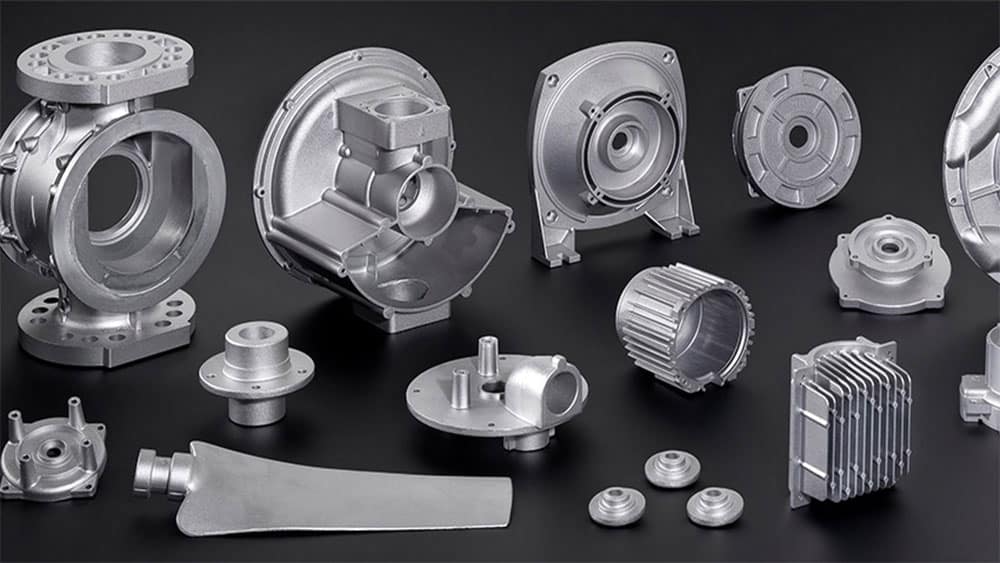

Die casting applications
Die casting is used in various industries. Some of its most important applications include:
Automotive industry: Production of engine parts, gearboxes, bodies and suspension system components.
Electronics industry: Manufacturing of housings for electronic devices such as smartphones and laptops.
Aerospace industry: Production of lightweight and durable parts for aircraft and satellites.
Home appliance production: Manufacturing of parts for washing machines, refrigerators and stoves.
Medical industry: Production of precision medical instruments and diagnostic equipment.
Difference between die casting and other casting methods
To better understand die casting, it is useful to compare it with other casting methods:
Sand casting: This method is less expensive, but its accuracy and surface quality are lower than die casting.
Gravity casting: In this method, molten metal is poured into a mold without pressure, which results in lower accuracy.
Centrifugal casting: Suitable for cylindrical parts, but has more design restrictions.
Die casting offers greater accuracy and speed than these methods due to the high pressure and use of metal molds.
Types of Metals Used in Die Casting
Choosing the right metal for die casting depends on the application of the part and the desired properties. The most common metals are:
Aluminum: lightweight, corrosion resistant, and suitable for automotive and aerospace parts.
Zinc: low melting point, suitable for small and complex parts.
Magnesium: the lightest die casting metal, ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
Copper: durable and suitable for electrical parts with high conductivity.

Important points in die casting mold design
Die casting mold design is one of the most important factors in the success of the die casting process. The following points should be considered:
Draft Angles: For easy removal of the part from the mold.
Cooling system: To control temperature and reduce solidification time.
Parting Lines: To separate the mold without damaging the part.
Gas evacuation system: To prevent gas cavities in the part.
New technologies in die casting
With the advancement of technology, new methods have been introduced to improve die casting:
Vacuum Die Casting: To reduce gas cavities and improve the quality of parts.
Automation and robotics: Increase speed and accuracy in production.
Computer simulation: Use software to predict the behavior of molten metal in the mold.
How to improve the quality of die casting parts?
To produce high-quality parts in die casting, several points should be considered:
Temperature control: The temperature of the metal and the mold must be optimal.
Proper pressure: The injection pressure must be adjusted according to the type of metal and the mold design.
Mold maintenance: Regular cleaning and repair of the molds prevents damage.
Component testing: Performing non-destructive tests such as X-rays to identify defects.
Die casting in Iran
In Iran, the die casting industry has grown significantly, especially in the automotive and industrial parts sectors. Several companies operate in the field of die casting parts production and, by utilizing modern technologies, have been able to meet the needs of domestic and even export markets. However, challenges such as high equipment costs and the need for specialized personnel still exist.
Conclusion
Die casting is one of the most efficient methods of producing metal parts with high precision and excellent quality. This process has a special place in various industries with advantages such as mass production, reduced waste, and variety of materials. However, the high initial cost and limitations such as part size must be taken into account. With the advancement of technology and the use of new methods, the future of die casting looks brighter than ever.